What is press forging?
Press forging may be defined as the process of shaping a metal that is placed between two dies by applying mechanical pressure or hydraulic pressure. Press forging is usually done on a forge press – a machine that applies gradual pressure on the forging dies. The shape of the metal is usually accomplished by a single stroke of the press for each die station.
Press forging may be undertaken as a hot or cold forging process. Press forging is suitable for high volume productivity of forgings. The various forging operations in a press forge and its applications are described below.
Process of Press Forging:
The forging done with the help of presses is known as press forging. It is usually referred as hot pressing, and is carried out either using hydraulic presses or mechanical (crank type) presses.
The press forging is similar to drop forging but uses a single, continuous, slow squeezing action instead of a series of impact blows. Because of slow ram travel and continuous action of the hydraulic presses, the deformation penetrates deeper so that the entire volume of the work piece simultaneously and uniformly undergoes plastic deformation. While in case of drop forging, the energy is only transmitted into the surface layers of the work part.
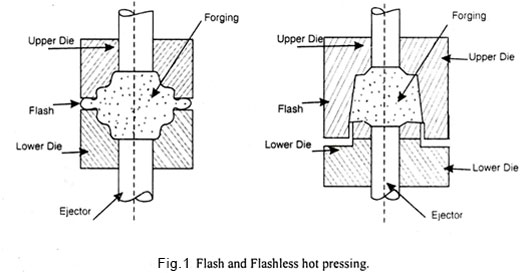
A good industrial practice is to use shaped blanks or preforms so that it can be forged in a single continuous stroke. The press forging may be of flash type of fleshless. In flash-press-forging, the surplus metal is flashed out in the gutter, provided at the parting line, while in flashless-press-forging, the entire material is utilized to fill the die cavity.
In both the processes, the forged part is pushed out of the die cavity by means of an ejector, as shown in Fig. 1:
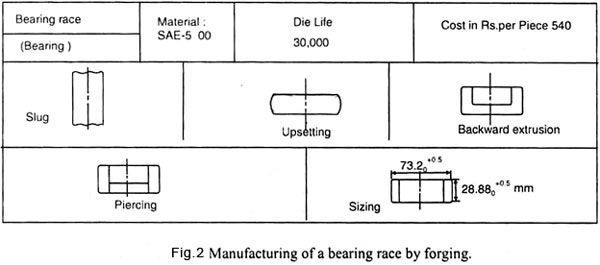
Both, hydraulic presses and mechanical presses are employed for press forging operation. The mechanical presses are used for light work while the hydraulic presses are employed for heavy work. Also, the mechanical press operates faster than the hydraulic presses but provides less squeezing force. Fig.2. Shows the sequence of operation, the estimated die life for production of bearing races.
Press forging is a method of forging that involves the slow and continuous pressure on the workpiece. This method differs greatly from the heavy and quick blows used in drop and hammer forging. The contact of the workpiece in the die is measured in seconds whereas drop forging and hammer forging is measured in milliseconds. Press forging can be carried out either hot or cold.
There are many advantages of press forges but the biggest is its ability to deform the workpiece. Hammer forging can only affect the surface of the workpiece whereas press forging can change the shape and interior of the workpiece at the same time. Press forging is a little more controlled than hammer forging and gives us a better knowledge of a part’s strain rate – that is how much pressure will cause manipulation of the part.
Another advantage of press forging is that it is more efficient. During hammer forging,the hammer absorbs a lot of the energy that could otherwise be focused on the workpiece. Press forging allows great efficiency and more control over the forging of the piece. Press forging can also be used to perform a number of different kinds of forging including impression-die press forging and open-die forging.